Table of Contents
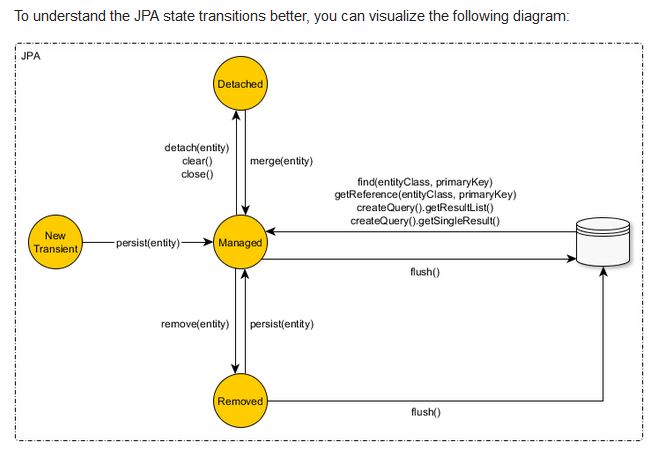
JPA State Transistion
JPA Method refresh()
- Uses Entity Manager refresh() method when you suspect that your data is changed in your database outside of an JPA operation
- The Entity itself must be in a managed status or you get IllegalArgumentException
- Entity Manager refresh() method allows us to revert back changes when a user decides to undo all local Entity operations .
Related JAVA Code tm = (TransactionManager)ctx.lookup("java:/TransactionManager"); setRunTimeInfo("Lookup Transactionmanager: ctx.lookup(java:/TransactionManager)"); String tx_status_before = returnTXStatus(tm); tm.begin(); String tx_status_after = returnTXStatus(tm); setRunTimeInfo("Begin Transaction: tm.begin() - Before " + tx_status_before + " - After " + tx_status_after ); em=getEntityManager(); e = em.find(Emp2.class, eno ); checkEntity(e,em); Transaction transaction = tm.suspend(); // Update via pure JDBC - data is already commited in an autonomous TX! setRunTimeInfo(" ------- Update Record via NON-XA datasource - outside from JPA Entity Mangager ----------"); doUpdate(e); setRunTimeInfo(" ------- Retrieving Data after doUpdate() ----------"); checkEntity(e,em); setRunTimeInfo(" Resuming transaction"); tm.resume(transaction); em.refresh(e); setRunTimeInfo(" ------- Retrieving Data after em.refesh() ----------"); checkEntity(e,em); tm.rollback(); setRunTimeInfo("After Resuming/rollback transaction"); checkEntity(e,em); setRunTimeInfo("The next em.refresh(e) should throw an execption as the Entity is not managed anymore"); em.refresh(e); Related Output: 11:16:07.453 Calling refreshEntity()in progress - ID: 9997 - useJoinTransaction : true 11:16:07.454 ------- Refresh test ---------- 11:16:07.454 Lookup Transactionmanager: ctx.lookup(java:/TransactionManager) 11:16:07.457 Begin Transaction: tm.begin() - Before [TM status: 6 - STATUS_NO_TRANSACTION] - After [TM status: 0 - STATUS_ACTIVE] 11:16:10.154 checkEntity() - : empno: 9997 - Sal: 2800 - Entity Salary Persistence : 2800 - Managed Entity Status : true - STALE Data: false 11:16:10.154 ------- Update Record via NON-XA datasource - outside from JPA Entity Mangager --------- 11:16:10.212 Leaving doUpdate() without Exceptions - Data commited ! 11:16:10.212 ------- Retrieving Data after doUpdate() ---------- 11:16:10.214 checkEntity() - : empno: 9997 - Sal: 2900 - Entity Salary Persistence : 2800 - Managed Entity Status : true - STALE Data: true 11:16:10.214 Resuming transaction 11:16:10.216 ------- Retrieving Data after em.refesh() ---------- 11:16:10.217 checkEntity() - : empno: 9997 - Sal: 2900 - Entity Salary Persistence : 2900 - Managed Entity Status : true - STALE Data: false 11:16:10.218 After Resuming/rollback transaction 11:16:10.219 checkEntity() - : empno: 9997 - Sal: 2900 - Entity Salary Persistence : 2900 - Managed Entity Status : false - STALE Data: false 11:16:10.220 The next em.refresh(e) should throw an execption as the Entity is not managed anymore 11:16:10.220 FATAL ERROR in refreshEntity(): 11:16:10.222 Potential Root Cause : Can not refresh not managed object: com.hhu.wfjpa2el.Emp2[ empno=9997 ]. 11:16:10.223 Leaving refreshEntity() - Entity manager closed ! Related Exception: 11:16:10.220 Error in top level function: refreshEntity() 11:16:10.221 Can not refresh not managed object: com.hhu.wfjpa2el.Emp2[ empno=9997 ]. 11:16:10.222 java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: Can not refresh not managed object: com.hhu.wfjpa2el.Emp2[ empno=9997 ]. at org.eclipse.persistence.internal.jpa.EntityManagerImpl.refresh(EntityManagerImpl.java:1024) at org.eclipse.persistence.internal.jpa.EntityManagerImpl.refresh(EntityManagerImpl.java:929) at com.hhu.wfjpa2el.JPATestBean.refreshEntity(JPATestBean.java:661) at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke0(Native Method)
Using Cache
There are two level of cache: L1, L2
- L1 is the Entitymanager Persistance Context.
- L2 is the EMF context .It can be shared with all Enitymanagers in the application
Cache Retrieval Mode The cache retrieval mode, set by the javax.persistence.retrieveMode property, controls how data is read from the cache for calls to the EntityManager.find method and from queries. The retrieveMode property can be set to one of the constants defined by the javax.persistence.CacheRetrieveMode enumerated type, either USE (the default) or BYPASS. When it is set to USE, data is retrieved from the second-level cache, if available. If the data is not in the cache, the persistence provider will read it from the database. When it is set to BYPASS, the second-level cache is bypassed and a call to the database is made to retrieve the data. Cache Store Mode The cache store mode, set by the javax.persistence.storeMode property, controls how data is stored in the cache. The storeMode property can be set to one of the constants defined by the javax.persistence.CacheStoreMode enumerated type, either USE (the default), BYPASS, or REFRESH. When set to USE the cache data is created or updated when data is read from or committed to the database. If data is already in the cache, setting the store mode to USE will not force a refresh when data is read from the database. When the store mode is set to BYPASS, data read from or committed to the database is not inserted or updated in the cache. That is, the cache is unchanged. When the store mode is set to REFRESH, the cache data is created or updated when data is read from or committed to the database, and a refresh is forced on data in the cache upon database reads. JPA Cache Details Enum CacheRetrieveMode Used as the value of the javax.persistence.cache.retrieveMode property to specify the behavior when data is retrieved by the find methods and by queries. CacheRetrieveMode BYPASS Bypass the cache: get data directly from the database. Since: JPA 2.0 CacheRetrieveMode USE Read entity data from the cache: this is the default behavior. Since: JPA 2.0 Enum CacheStoreMode Used as the value of the javax.persistence.cache.storeMode property to specify the behavior when data is read from the database and when data is committed into the database. CacheStoreMode BYPASS Don't insert into cache. Since: JPA 2.0 CacheStoreMode REFRESH Insert/update entity data into cache when read from database and when committed into database. Forces refresh of cache for items read from database. Since: JPA 2.0 CacheStoreMode USE Insert/update entity data into cache when read from database and when committed into database: this is the default behavior. Does not force refresh of already cached items when reading from database. Since: JPA 2.0
JPA and Object Comparison
- Note the Netbeans ORM tool creates code only to compare the PK field.
You need to extend the equals function to cover add. fields .
Sample adding the sal field for object comparison:
public class Emp2 implements Serializable
{
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
@Id
@Basic(optional = false)
@NotNull
@Column(name = "EMPNO"
...
@Override
public boolean equals(Object object)
{
// TODO: Warning - this method won't work in the case the id fields are not set
if (!(object instanceof Emp2))
{
return false;
}
Emp2 other = (Emp2) object;
if ((this.empno == null && other.empno != null) || (this.empno != null && !this.empno.equals(other.empno)))
{
return false;
}
// Newly added to extend equals method to check sal fied too.
if ((this.sal == null && other.sal != null) || (this.sal != null && !this.sal.equals(other.sal)))
{
return false;
}
return true;
}
Using JTA and Entity Manager [ see Pro JPA2 – page 129 ]
- If the Persistence Manager is created outside the transaction ( before ut.begin() ) we need to join the transaction using by using em.joinTransaction(); - Without joining you very likely see following error: 09:38:33.272 Cannot call methods requiring a transaction if the entity manager has not been joined to the current transaction. 09:38:33.272 javax.persistence.TransactionRequiredException: Cannot call methods requiring a transaction if the entity manager has not been joined to the current transaction. at org.eclipse.persistence.internal.jpa.EntityManagerImpl.checkForTransaction(EntityManagerImpl.java:2045) at org.eclipse.persistence.internal.jpa.EntityManagerImpl.flush(EntityManagerImpl.java:863) at com.hhu.wfjpa2el.JPATestBean.runJPA(JPATestBean.java:201) at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke0(Native Method) Current Code: em=getEntityManager(); ut.begin(); em.joinTransaction(); em.persist(e); em.flush(); ut.commit(); Workaround 1 : Create the Entity Manager after ut.begin() ut.begin(); em=getEntityManager(); em.persist(e); em.flush(); ut.commit(); Workaround 2: Use em.joinTransaction() em=getEntityManager(); ut.begin(); em.joinTransaction(); em.persist(e); em.flush(); ut.commit();
JPA and Anotations
JAXP Anotations
@XmlRootElement Define the root element for the XML to be produced with @XmlRootElement JAXB annotation @XmlAccessorType(XmlAccessType.FIELD) Defined at class level. Annotate private fields instead of getter methods. @XmlTransient Annotate fields that we do not want to be included in XML or JSON output with @XMLTransient.
JPA Anotations
@Entity annotation defines that a class can be mapped to a table @Id Marks a field as a Primary Key. Requirement @GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.TABLE, generator = "accountSequence") Use a sequence to AUTO generate Primary Keys
Anotation Sample
@Entity
@XmlRootElement
@XmlAccessorType(XmlAccessType.FIELD)
@Table(name = "Account")
public class Account extends AbstractBaseEntity {
public Account() {
publishers = new LinkedList<>();
}
/**
* Primary key.
*/
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.TABLE, generator = "accountSequence")
@TableGenerator(name = "accountSequence")
@XmlTransient
private Long id;
/**
* The login name of the user.
* Is different form user real name. Normally this value is taken from external
* authentication system e.g. LDAP.
*/
@NotNull
@Column(nullable = false, length = 45, unique = true)
private String loginName;
- Field id is anotated with @XmlTransient and will not be included in the XML / JSON Outout
- Field loginName is NOT anotated with @XmlTransient and bnot be included in the XML / JSON Outout
Reference
JPA @OneToManyRelationshiip
- The best way to map a @OneToMany relationship with JPA and Hibernate
- How to synchronize bidirectional entity associations with JPA and Hibernate
- Hibernate One to Many Annotation Tutorialn
Hibernate One to Many Annotation Tutorial
JPA System errors: javax.ejb.EJBTransactionRolledbackException
Error
[2018-11-07T14:22:58.273+0100] [Payara 5.182] [WARNING] [AS-EJB-00056] [javax.enterprise.ejb.container] [tid: _ThreadID=38 _ ThreadName=http-thread-pool::http-listener-1(4)] [timeMillis: 1541596978273] [levelValue: 900] [[ A system exception occurred during an invocation on EJB SemesterService, method: public int de.thnuernberg.in.stuv.pythia.app.services.SemesterService.retrieveSemesterData(int)]] [2018-11-07T14:22:58.273+0100] [Payara 5.182] [WARNING] [] [javax.enterprise.ejb.container] [tid: _ThreadID=38 _ ThreadName=http-thread-pool::http-listener-1(4)] [timeMillis: 1541596978273] [levelValue: 900] [[ javax.ejb.EJBTransactionRolledbackException at com.sun.ejb.containers.BaseContainer.mapLocal3xException(BaseContainer.java:2390) at com.sun.ejb.containers.BaseContainer.postInvoke(BaseContainer.java:2172) at com.sun.ejb.containers.BaseContainer.postInvoke(BaseContainer.java:2093)
Explanation
Any exception that is a subclass of Exception, but not a subclass of RuntimeException and RemoteException, is an application exception. All the application exceptions are checked exceptions, So, when we call another method in our method that can throw an application exception, we must either declare it in the throws clause of the calling method or catch it in the body of the calling method or both. All system exceptions are unchecked exceptions except RemoteExceptions and it can't be handled by the user.
Root Cause
- Drop Table command when the JTA Datasource was still connected !
- Note int this cause data from Entity Manager and Database are not in sync anymore
- A not catchable System Execption is thrown and only a Webserver reboot will fix the db/entity manager integrity
Fix
- Restart Payara !
Reference
- Most of the material for this blog is a result of reading the wonderful book : Pro JPA 2 [ Mike Keith and Marrik Schincariol – I would recommend reading it if you want more indepth knowledge of how JPA works ]
- Manipulating Entities with EntityManager
- JPA (Java Persistence API :
- JPA/JDBC Overview
- JPA and BMT Transactions